Research is an essential part of advancing knowledge and understanding phenomena. There are two main approaches to conducting research: qualitative and quantitative. Understanding the difference between these two types of research is key to determining which approach is best suited for a particular research problem.

What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research aims to understand why and how people react in certain situations. It relies on non-numerical data like words, photos, videos, and other formats that do not involve math and statistics.
Data Collection in Qualitative Research
Some common qualitative data collection methods include:
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Observation
- Case studies
- Qualitative surveys
The goal is to collect in-depth insights on behaviors, experiences, and perspectives that cannot be fully understood through numbers alone.
Analysis of Qualitative Data
Qualitative data analysis examines non-numerical information for common patterns and themes that help explain why study participants responded the way they did. There is more subjectivity in interpreting qualitative data compared to quantitative data.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research aims to quantify behaviors, opinions, and other defined variables using numbers and statistical analysis. The goal is to test theories and hypotheses, establish facts, and make predictions that can be generalized to larger populations.
Data Collection in Quantitative Research
Some common quantitative data collection methods include:
- Structured surveys with closed-ended questions
- Experiments that test cause-effect hypotheses
- Analysis of secondary numerical datasets
The focus is on gathering hard, measurable evidence that can be statistically analyzed.
Analysis of Quantitative Data
Powerful statistical software makes it possible to analyze large volumes of quantitative data. Results are presented numerically and visually through graphs, charts, and tables. Statistical analysis looks for statistically significant relationships between variables being studied.
Key Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
While both methods aim to describe and understand research problems, there are fundamental differences between these two approaches:
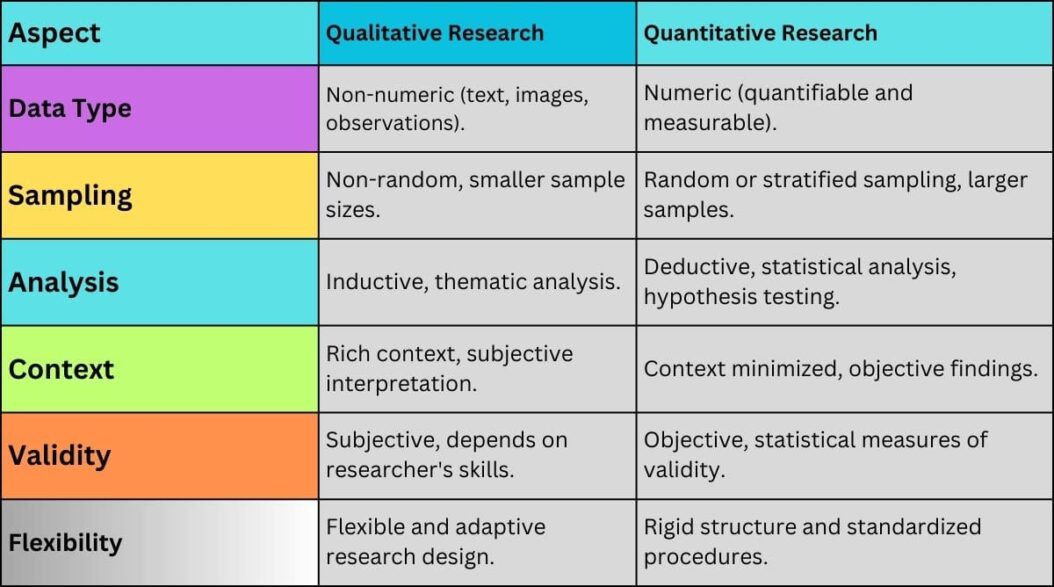
Purpose and Goals
- Qualitative research: Gain in-depth understanding of human behaviors and reasons driving such behaviors
- Quantitative research: Test hypotheses, analyze cause-effect relationships, generalize results to wider populations
Type of Data Collected
- Qualitative data: Non-numerical, unstructured data from interviews, images, video, documents
- Quantitative data: Numerical, structured data from surveys, sensors, website analytics, etc.
Sample Size
- Qualitative studies: Smaller sample size that fits the purpose of research
- Quantitative studies: Larger sample size that represents target population
Type of Analysis
- Qualitative analysis: Subjective interpretation of data for themes and patterns
- Quantitative analysis: Objective statistical testing for significant relationships
Results
- Qualitative findings: Detailed insights presented verbally and visually
- Quantitative findings: Numerical statistics and metrics summarized graphically
Choosing Between Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
There are several factors guiding the decision to adopt a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods approach:
Research Goals
- Exploratory research aiming to capture detailed insights should take a qualitative approach
- Studies testing theories or hypotheses are best suited for quantitative methods
Available Resources and Skills
- Qualitative research requires strong writing and analytical skills
- Quantitative research needs advanced statistical skills and analysis software
Sensitivity of Research Topic
- Studying personal or controversial topics may benefit more from building trust in qualitative studies versus anonymous quantitative surveys
Level of Understanding of Topic
- Less understood phenomena warrant initial qualitative exploration before quantitative confirmation
- Well-researched topics can move directly to quantitative hypothesis testing
By considering these decision factors, researchers can determine whether to design qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods research that aligns with study goals.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Both research approaches have unique strengths and weaknesses that must be weighed when deciding which methodology to use.
Qualitative Research: Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Provides depth and detail that quantitative lacks
- Flexible to iterate approach based on discoveries
- Context-specific insights
Weaknesses
- No basis for wider generalization
- Resource intensive data collection and analysis
- Subject to researcher bias
Quantitative Research: Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Provides objective, numerical data
- Results can be generalized to larger populations
- Establishes cause-effect relationships
Weaknesses
- May miss contextual details
- Inflexible and narrow in focus
- Resource intensive data analysis
By understanding these inherent trade-offs, researchers can combine these approaches through mixed methods to leverage their complementary strengths.
Examples Comparing Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Let’s compare how these two research approaches are applied through examples around two hypothetical research topics.
Experience of High School Dropouts
Qualitative Approach
- In-depth interviews of 15-20 high school dropouts exploring their personal stories and challenges behind dropping out
Quantitative Approach
- Structured survey of 500 high school dropouts around contributing factors and trends leading to dropping out
Effect of Tutoring on Academic Performance
Qualitative Approach
- Case studies analyzing 10-15 students’ perceptions of how tutoring impacted their learning and growth
Quantitative Approach
- Experiment with 100 students receiving tutoring interventions to measure changes in GPAs between treatment and control groups
These examples illustrate how qualitative research uncovers personal narratives while quantitative research seeks generalizable, hard evidence around topics of study.
Mixing Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research bring unique strengths and weaknesses. Using mixed methods combines these approaches to provide:
- Initial qualitative exploration to determine behaviors, attitudes, and concepts
- Follow up quantitative research with larger samples to test qualitative findings
- Corroboration between qualitative and quantitative data to strengthen insights
For example, focus groups may discover consumer needs while structured surveys measure needs prevalence. Or, case studies can reveal patient treatment barriers while clinical trials assess intervention efficacy.
Mixed methods provide completeness and corroboration to research conclusions.
Choosing the Right Research Approach
Deciding between qualitative vs quantitative research approaches depends greatly on the research problem being addressed. By clearly defining study goals, resources, data requirements, and analysis needs, researchers can determine if a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods approach will provide the evidence needed to arrive at compelling conclusions.
Qualitative research excels at exploring the “why” while quantitative research provides the concrete, measurable evidence around “what”. When combined effectively through mixed method designs, these approaches provide powerful means to gaining actionable insights.
Conclusion
Qualitative and quantitative research represent distinct but complementary investigatory techniques for advancing knowledge. While qualitative inquiry reveals deeper understandings through subjective interpretation, quantitative measures facilitate broader applications of findings through statistical testing. Determining appropriate applications of each based on well-defined research problems, available data sources, timeline constraints, sample population accessibility, analytical capabilities, and infrastructure resources enables organizations to strategically conduct studies suited for their objectives, budget, and skills. With a vast spectrum of research goals and contexts, harnessing these multidimensional lenses expands humanity’s knowledge base for the betterment of individuals, communities, systems, policies, technologies, and beyond.
FAQs
What are some key differences between qualitative and quantitative research?
Some key differences are the type of data collected (non-numerical for qualitative, numerical for quantitative); sample size (smaller for qualitative, larger that represents target population for quantitative); and analysis approach (subjective interpretation for themes for qualitative, statistical testing for relationships for quantitative).
When should qualitative research methods be used versus quantitative methods?
Qualitative methods help gain detailed understanding of personal experiences and explain behaviors when exploring a problem. Quantitative methods test hypotheses and find measurable evidence when variables and relationships are known.
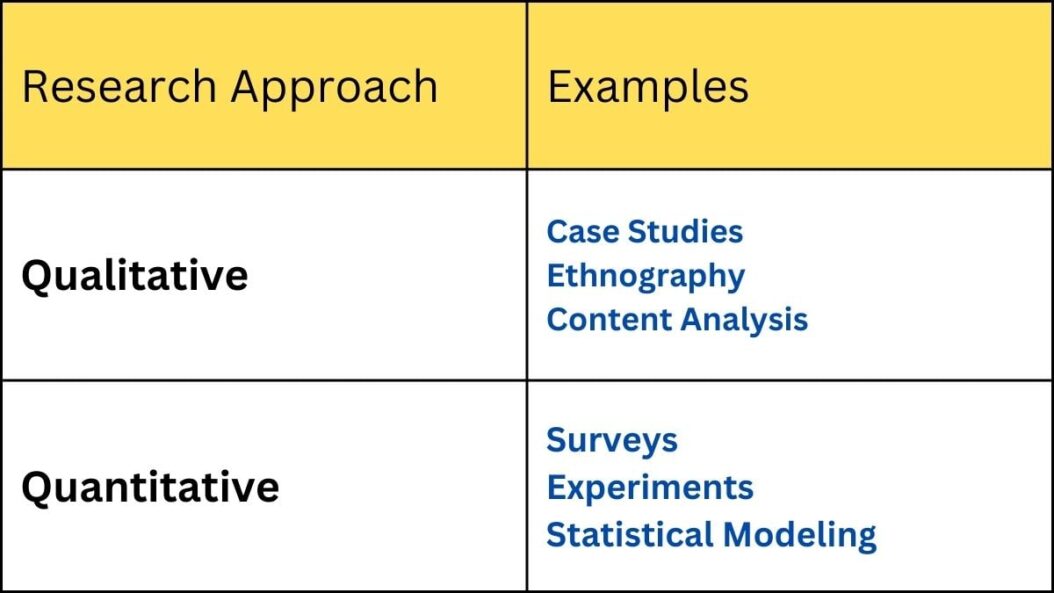
What are some examples of qualitative research versus quantitative research?
Qualitative research examples include in-depth interviews, ethnographic observations, and case study analysis. Quantitative examples include surveys, controlled experiments, and analysis of numerical datasets.
Why would a mixed methods design be used instead of just qualitative or quantitative?
Mixed methods provide an initial qualitative exploration to discover behaviors and attitudes, followed by quantitative confirmation of qualitative findings with larger samples. This combination leverages strengths of both approaches.
What are some best practices for determining appropriate research methods?
Clearly define research goals, data needs, resources, sample access, analytical capabilities, and timeline to guide methodology. Qualitative methods capture details and insights but do not generalize. Quantitative facilitates deductions with statistical analysis but misses qualitative details.
- Top 10 AI Image Generators Without Censorship 2025 - July 2, 2025
- How Shopping Habits Transform with AI in 2025 - June 29, 2025
- Your Organization’s Data Cannot Be Pasted Here: Complete Solutions Guide for 2025 - June 24, 2025
