Accessing Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows 10/11 is essential for executing commands that need elevated privileges. From system repairs to network configurations, this guide outlines ten simple methods using the Start Menu, Search Bar, Task Manager, and more – to quickly and efficiently open Command Prompt with admin rights in both Windows 10 and Windows 11, when needed.
Why Run Command Prompt as Administrator?
Before we dive into the methods, it’s important to understand why you might need to run Command Prompt as an administrator. Administrative privileges allow you to execute commands that can make significant changes to your system, such as:
- Installing or uninstalling programs
- Modifying system files
- Changing network configurations
- Running advanced troubleshooting tools
Now, let’s explore the various ways to open Command Prompt with elevated privileges.
Method 1: Using the Start Menu
Quick and Easy Access
One of the simplest ways to open Command Prompt as an administrator is through the Start menu. Here’s how:
- Click on the Start button or press the Windows key.
- Type “cmd” in the search bar.
- Right-click on “Command Prompt” in the search results.
- Select “Run as administrator” from the context menu.
This method works consistently across both Windows 10 and Windows 11, making it a reliable choice for users of either operating system.
Method 2: Windows PowerShell
Leveraging PowerShell for Command Prompt Access
Windows PowerShell, a more advanced command line interface, can also be used to open Command Prompt with administrative rights:
- Press Win + X to open the Quick Access menu.
- Select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” or “Terminal (Admin)” in Windows 11.
- In the PowerShell window, type “start cmd” and press Enter.
This method opens a regular Command Prompt. To open it as an administrator directly from PowerShell, use the following command:
Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAsMethod 3: Task Manager
The Hidden Gem for Administrative Tools
Task Manager isn’t just for ending unresponsive programs; it can also launch Command Prompt with elevated privileges:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click on “File” in the menu bar.
- Select “Run new task.”
- Type “cmd” in the dialog box.
- Check the box that says “Create this task with administrative privileges.”
- Click “OK.”
This method is particularly useful when other parts of the Windows interface are not responding correctly.
Method 4: File Explorer
Navigating to Command Prompt’s Location
For those who prefer a more visual approach, File Explorer offers a way to launch Command Prompt as an administrator:
- Open File Explorer (Win + E).
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32.
- Locate “cmd.exe” in the list of files.
- Right-click on “cmd.exe.”
- Choose “Run as administrator.”
This method allows you to see the actual executable file, which can be helpful for troubleshooting or creating shortcuts.
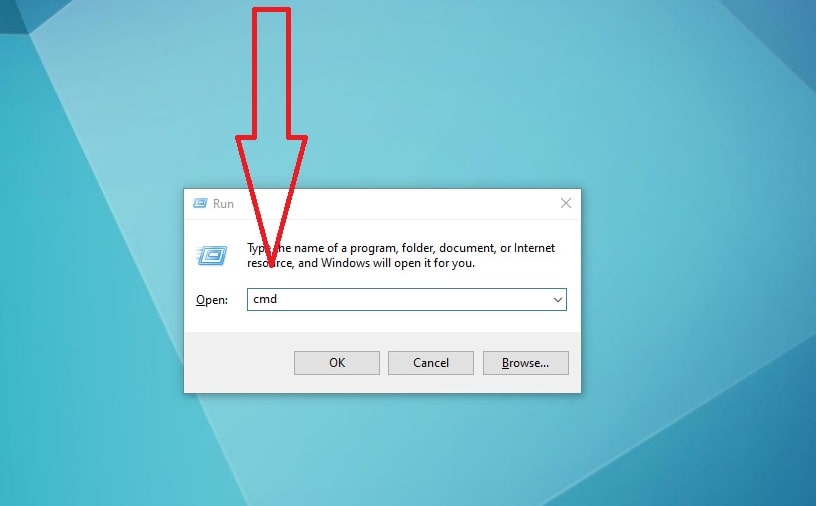
Method 5: Run Dialog
The Classic Approach
The Run dialog has been a part of Windows for decades and remains a quick way to open Command Prompt:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type “cmd” and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
Using Ctrl + Shift + Enter instead of just Enter automatically requests administrative privileges, saving you an extra step.
Method 6: Desktop Shortcut
Creating a Custom Administrator Command Prompt Shortcut
For frequent users, creating a desktop shortcut can be a time saver:
- Right-click on an empty area of the desktop.
- Select New > Shortcut.
- In the location field, type:
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe - Click “Next” and name your shortcut (e.g., “Admin CMD”).
- Right-click on the new shortcut and select “Properties.”
- In the “Shortcut” tab, click “Advanced.”
- Check the box for “Run as administrator.”
- Click “OK” and then “Apply.”
Now you have a dedicated shortcut that always opens Command Prompt with administrative rights.
Method 7: Task Scheduler
Automating Administrative Command Prompt Access
For more advanced users, Task Scheduler can be used to create a task that opens Command Prompt as an administrator:
- Open Task Scheduler (search for it in the Start menu).
- Click “Create Task” in the right panel.
- Name the task (e.g., “Admin CMD”).
- Check “Run with highest privileges.”
- Go to the “Actions” tab and click “New.”
- Set the action to “Start a program.”
- In the “Program/script” field, enter:
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe - Click “OK” to save the task.
You can now run this task whenever you need an elevated Command Prompt.
Method 8: Windows Terminal
The Modern Command Line Experience
Windows Terminal, introduced in recent years, offers a more customizable command-line interface:
- Install Windows Terminal from the Microsoft Store if you haven’t already.
- Open Windows Terminal.
- Click the downward arrow next to the new tab button.
- Select “Command Prompt” under the “Run as administrator” section.
Windows Terminal allows you to have multiple command line tools open in tabs, including both regular and administrative Command Prompts.
Method 9: WinX Menu
The Power User’s Quick Access Menu
The WinX menu (also known as the Power User menu) provides quick access to various system tools:
- Press Win + X or right-click the Start button.
- Select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows Terminal (Admin)” in Windows 11.
If you don’t see Command Prompt in this menu, it may have been replaced by PowerShell. You can change this in Windows settings.
Method 10: Cortana or Search Bar
Voice Activated or Type to Search Method
For those who prefer voice commands or quick typing:
- Click on the search bar or Cortana icon in the taskbar.
- Type or say “Command Prompt.”
- In the search results, click “Run as administrator” on the right side.
This method combines the simplicity of search with the specificity of requesting administrative access.
Comparison Table of Methods
To help you choose the best method for your needs, here’s a comparison table:
| Method | Ease of Use | Speed | Customizability | Works on Win 10 | Works on Win 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Menu | High | Fast | Low | Yes | Yes |
| PowerShell | Medium | Medium | High | Yes | Yes |
| Task Manager | Medium | Medium | Low | Yes | Yes |
| File Explorer | Low | Slow | Medium | Yes | Yes |
| Run Dialog | High | Fast | Low | Yes | Yes |
| Desktop Shortcut | High | Fast | High | Yes | Yes |
| Task Scheduler | Low | Medium | High | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Terminal | Medium | Fast | High | Yes | Yes |
| WinX Menu | High | Fast | Low | Yes | Yes |
| Cortana/Search | High | Medium | Low | Yes | Yes |
Compatibility and Security Considerations
While these methods work on both Windows 10 and Windows 11, it’s important to note that Microsoft regularly updates its operating systems. Always ensure you’re running the latest version of Windows to have access to the most current features and security enhancements.
When using Command Prompt with administrative privileges, exercise caution. Elevated access allows you to make significant changes to your system, which can potentially cause issues if not done correctly. Always double check commands before executing them, and consider creating a system restore point before making major changes.
Conclusion
Mastering the various ways to open Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows 10 and 11 can significantly enhance your productivity and troubleshooting capabilities. Whether you prefer GUI methods like the Start menu and File Explorer, or more advanced techniques like PowerShell and Task Scheduler, there’s an option suited for every user’s preference and technical skill level.
Remember, with great power comes great responsibility. Always use administrative privileges judiciously and keep your system updated to ensure the best performance and security. Happy commanding!
FAQs
Can I make Command Prompt always run as an administrator by default?
Yes, you can modify the shortcut properties to always run as administrator, but this is not recommended for security reasons. It’s better to elevate privileges only when necessary.
Is there a keyboard shortcut to open Command Prompt as an administrator directly?
There’s no built-in keyboard shortcut, but you can create a custom one using Auto Hot key or by assigning a shortcut key to a desktop shortcut configured to run as administrator.
How does Windows 11 differ from Windows 10 in terms of accessing Command Prompt as an administrator?
Windows 11 generally favors Windows Terminal over Command Prompt in some menus, but the core methods remain largely the same. The WinX menu in Windows 11 typically shows “Windows Terminal (Admin)” instead of “Command Prompt (Admin).”
Are there any risks to running Command Prompt as an administrator?
Yes, running as an administrator gives you the ability to make system wide changes, which can potentially harm your system if used incorrectly. Always be cautious and verify commands before executing them.
Can I use these methods to open PowerShell as an administrator as well?
Yes, most of these methods can be adapted to open PowerShell with administrative privileges by replacing “cmd” with “powershell” in the relevant steps.
- What is One Challenge in Ensuring Fairness in Generative AI: The Hidden Bias Problem - August 15, 2025
- How Small Language Models Are the Future of Agentic AI - August 15, 2025
- What Are the Four Core Characteristics of an AI Agent? - August 15, 2025
